High-resolution structure determination using high-throughput electron cryo-tomography
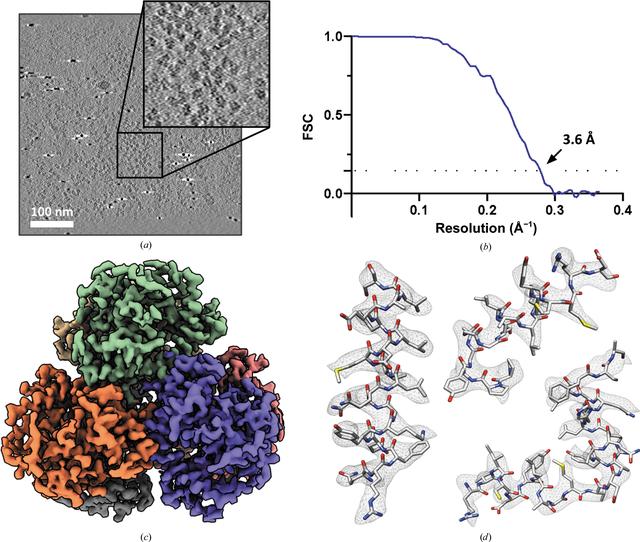
The low throughput characteristic of tomographic data acquisition combined with the complex data-analysis pipeline that is required to obtain high-resolution maps, has limited the applicability of this technique to favorable samples or to resolutions that are too low to provide useful mechanistic information. Recently, beam image-shift electron cryo-tomography (BISECT), a strategy to significantly accelerate the acquisition of tilt series without sacrificing image quality, was introduced. The ability to produce thousands of high-quality tilt series during a single microscope session, however, introduces significant bottlenecks in the downstream data analysis, which has so far relied on specialized pipelines. Here, recent advances in accurate estimation of the contrast transfer function and self-tuning exposure-weighting routines that contribute to improving the resolution and streamlining the structure-determination process using sub-volume averaging are reviewed. Ultimately, the combination of automated data-driven techniques for image analysis together with high-throughput strategies for tilt-series acquisition will pave the way for tomography to become the technique of choice for in situ structure determination.
| Abstract | Tomographic reconstruction of frozen-hydrated specimens followed by extraction and averaging of sub-tomograms has successfully been used to determine the structure of macromolecules in their native environment at resolutions that are high enough to reveal molecular level interactions. The low throughput characteristic of tomographic data acquisition combined with the complex data-analysis pipeline that is required to obtain high-resolution maps, however, has limited the applicability of this technique to favorable samples or to resolutions that are too low to provide useful mechanistic information. Recently, beam image-shift electron cryo-tomography (BISECT), a strategy to significantly accelerate the acquisition of tilt series without sacrificing image quality, was introduced. The ability to produce thousands of high-quality tilt series during a single microscope session, however, introduces significant bottlenecks in the downstream data analysis, which has so far relied on specialized pipelines. Here, recent advances in accurate estimation of the contrast transfer function and self-tuning exposure-weighting routines that contribute to improving the resolution and streamlining the structure-determination process using sub-volume averaging are reviewed. Ultimately, the combination of automated data-driven techniques for image analysis together with high-throughput strategies for tilt-series acquisition will pave the way for tomography to become the technique of choice for in situ structure determination. |
|---|