Skip to content
-
-
- Cryo-EM, Methods, Publications
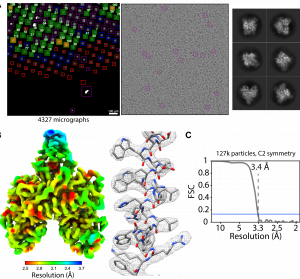
- Data-driven determination of number of discrete conformations in single-particle cryo-EM Single-particle cryo-EM can be used to image heterogeneous samples containing multiple molecular species, different oligomeric states or distinct conformations. This, however, requires expert-user knowledge and trial-and-error experimentation to determine the correct number of conformations present in a mixture. Here, we propose an approach to address the problem of automatically…
-
-
- Publications, Structures
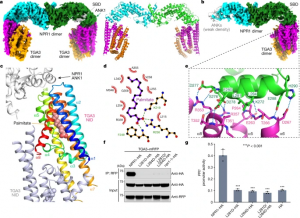
- Structural basis of NPR1 in activating plant immunity We report cryo-electron microscopy and crystal structures of Arabidopsis NPR1 and its complex with the transcription factor TGA3. Cryo-electron microscopy analysis reveals that NPR1 is a bird-shaped homodimer comprising a central Broad-complex, Tramtrack and Bric-à-brac (BTB) domain, a BTB and carboxyterminal Kelch helix bundle, four ankyrin repeats and a disordered salicylic-acid-binding…
-
-
- Cryo-EM, Machine learning and artificial intelligence, Methods, Publications
- Automated systematic evaluation of cryo-EM specimens with SmartScope We present SmartScope, the first framework to streamline, standardize, and automate specimen evaluation in cryo-electron microscopy. SmartScope employs deep-learning-based object detection to identify and classify features suitable for imaging, allowing it to perform thorough specimen screening in a fully automated manner. A web interface provides remote control over the automated operation…
-
-
- HIV, Membrane Proteins, Publications, Structures
- Fab-dimerized glycan-reactive antibodies are a structural category of natural antibodies Natural antibodies (Abs) can target host glycans on the surface of pathogens. We studied the evolution of glycan-reactive B cells of rhesus macaques and humans using glycosylated HIV-1 envelope (Env) as a model antigen. We describe HIV-1 Env Fab-dimerized glycan (FDG)-reactive neutralizing Abs in HIV-1 vaccinated and simian-HIV (SHIV)-infected…
-
-
- Cryo-EM, Machine learning and artificial intelligence, Methods, Publications
- Cryo-ZSSR: multiple-image super-resolution based on deep internal learning We present a multiple-image super-resolution (SR) algorithm based on deep internal learning designed specifically to work under low-SNR conditions typical of cryo-EM data. Our approach leverages the internal image statistics of cryo-EM movies and does not require training on ground-truth data. When applied to a single-particle dataset of apoferritin, we show…
-
-
- Cryo-EM, Methods, Publications
- Beam image-shift accelerated data acquisition for near-atomic resolution single-particle cryo-electron tomography To overcome the inherent low-throughput characteristic of CET data collection, improve the resolution of SVA and extend its application to a wider set of samples including low molecular weight targets, here, we: (1) use beam-image shift navigation to multiply the number of regions of interest imaged at each…
-
-
- CRISPR, Publications, Structures
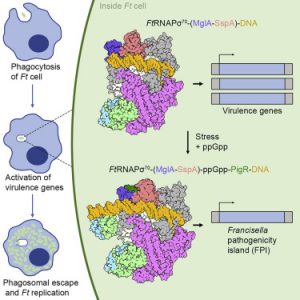
- Structural Basis for Virulence Activation of Francisella tularensis The bacterium Francisella tularensis (Ft) is one of the most infectious agents known. Ft virulence is controlled by a unique combination of transcription regulators: the MglA-SspA heterodimer, PigR, and the stress signal, ppGpp. MglA-SspA assembles with the σ70-associated RNAP holoenzyme (RNAPσ70), forming a virulence-specialized polymerase. These factors activate Francisella pathogenicity island…
-
-
- Publications, Ribosome, Structures
- Structural impact of K63 ubiquitin on yeast translocating ribosomes under oxidative stress K63 ubiquitination of ribosomes serves as a key regulator of protein production during cellular exposure to oxidative stress. Defining the structural and functional mechanisms of translation regulation would support the current understanding of critical reprogramming of eukaryotic gene expression. Our paper presents an examination of the structure…