Skip to content
-
-
-
- Cancer, Publications, Structures
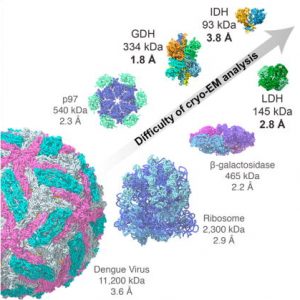
- Breaking Cryo-EM Resolution Barriers to Facilitate Drug Discovery Using cryo-EM we were able to capture images of glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH), an enzyme found in cells, at a resolution of 1.8 angstroms, a level of detail at which the structure of the central parts of the enzyme could be visualized in atomic detail. We also imaged two small proteins in…
-
-
- Cancer, Publications, Structures
- 2.3 Å Resolution Cryo-EM Structure of Human p97 and Mechanism of Allosteric Inhibition The protein p97 is an AAA adenosine triphosphatase (ATPase) that uses energy from ATP hydrolysis to regulate substrates involved in intracellular protein quality control. Its role in this central process makes it a target for cancer chemotherapy. We used cryo-electron microscopy to determine high-resolution structures for…
-
-
- Cancer, Publications, Structures
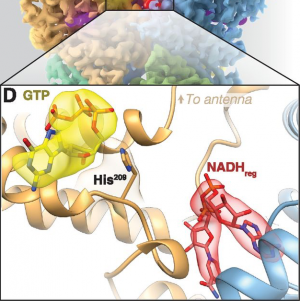
- Using Cryo-EM to Map Small Ligands on Dynamic Metabolic Enzymes: Studies with Glutamate Dehydrogenase Molecular Pharmacology, 89 (6) 645-651, 2016.
-
-
-
- Membrane Proteins, Publications, Structures
- Cryo-electron Microscopy Structures of Chimeric Hemagglutinin Displayed on a Universal Influenza Vaccine Candidate Chimeric hemagglutinin proteins are set to undergo human clinical trials as a universal influenza vaccine candidate, yet no structural information for these proteins is available. Using cryo-electron tomography, we report the first three-dimensional (3D) visualization of chimeric hemagglutinin proteins displayed on the surface of the influenza…
-
-
- Membrane Proteins, Publications, Structures
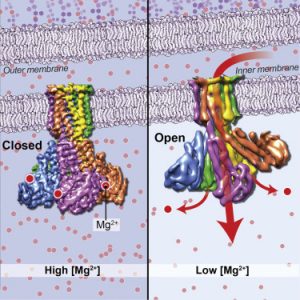
- Cryo-EM Structures of the Magnesium Channel CorA Reveal Symmetry Break upon Gating Magnesium ions (Mg2+) play essential roles in all living organisms. Bacteria and other prokaryotes rely upon the Mg2+-dependent channel CorA, which is composed of five identical subunits (A-E), to obtain these ions from their surroundings. Studies of CorA showed that, in contrast to most ligand-gated ion channels,…
-
-
- Publications, Structures, β-galactosidase
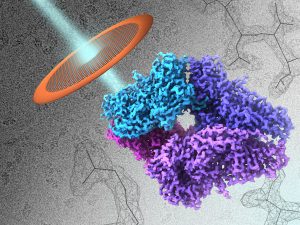
- 2.2 Å Resolution Cryo-EM Structure of β-galactosidase in Complex with a Cell-permeant Inhibitor Recent advances in cryo–electron microscopy allow structures of large macromolecules to be determined at near-atomic resolution. So far, though, resolutions approaching 2 Å, where features key to drug design are revealed, remain the territory of x-ray crystallography. Bartesaghi et al. achieved a resolution of 2.2 Å for a…