Skip to content
-
-
- Cryo-EM, Methods, Publications
- Mathematical Theory, Computational Challenges, and Opportunities Structural biology studies the structure and dynamics of macromolecules to broaden our knowledge about the mechanisms of life and impact the drug-discovery process. Owing to recent groundbreaking developments, chiefly in hardware technologies and data processing techniques, many new molecular structures have been elucidated to near-atomic resolutions using cryo-EM. The main goal of this article…
-
-
- HIV, Publications, Structures
- Disruption of the HIV-1 Envelope allosteric network blocks CD4-induced rearrangements The trimeric HIV-1 Envelope protein (Env) mediates viral-host cell fusion via a network of conformational transitions, with allosteric elements in each protomer orchestrating host receptor-induced exposure of the co-receptor binding site and fusion elements. To understand the molecular details of this allostery, here, we introduce Env mutations aimed to…
-
-
- Cryo-EM, Machine learning and artificial intelligence, Methods, Publications
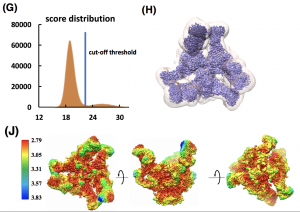
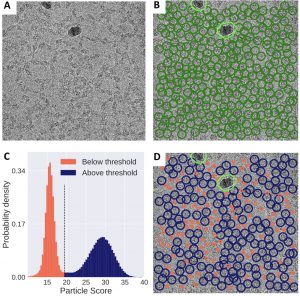
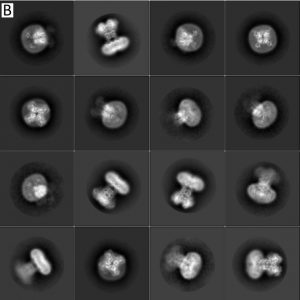
- Unsupervised particle sorting for high-resolution single-particle cryo-EM Single-particle cryo-Electron Microscopy (EM) has become a popular technique for determining the structure of challenging biomolecules that are inaccessible to other technologies. Recent advances in automation, both in data collection and data processing, have significantly lowered the barrier for non-expert users to successfully execute the structure determination workflow. Many critical data processing…
-
-
- Membrane Proteins, Publications, Structures
- Single-particle cryo-EM structure of a voltage-activated potassium channel in lipid nanodiscs The structure of a voltage-activated potassium channel in lipid nanodiscs solved using cryo-electron microscopy is similar to previous X-ray structures, and provides insights into the mechanism of C-type inactivation. eLife, 7:e37558, 2018.
-
-
- Membrane Proteins, Publications, Structures
- Cryo-EM structure of human rhodopsin bound to an inhibitory G protein For the first time, scientists have visualized the interaction between two critical components of the body’s vast cellular communication network, a discovery that could lead to more effective medications with fewer side effects for conditions ranging from migraine to cancer. The near-atomic resolution images obtained, show a G-protein coupled…
-
-
- Cryo-EM, Methods, Publications
- Atomic Resolution Cryo-EM Structure of B-galactosidase We report methods to account for radiation damage and local changes in defocus and image drift, enabling visualization of atomic resolution features in a cryo-EM density map of inhibitor-bound b-galactosidase, and measuring of local flexibility of the bound inhibitor using constrained molecular dynamics simulations. Structure, 26(6), 2018.
-
-
- Publications, Structures, β-galactosidase
- Atomic Resolution Cryo-EM Structure of B-galactosidase We report methods to account for radiation damage and local changes in defocus and image drift, enabling visualization of atomic resolution features in a cryo-EM density map of inhibitor-bound -galactosidase, and derivation of atom-specific measures of local flexibility of the bound inhibitor using constrained molecular dynamics simulations. Structure, 26(6), p. 848-85, 2018.
-
-
- CRISPR, Publications, Structures
- Cryo-EM Structures Reveal Mechanism and Inhibition of DNA Targeting by a CRISPR-Cas Surveillance Complex Electron-microscopy images reveal how a CRISPR system marks specific DNA sequences for destruction. Microbes use CRISPR as a defense system to fend off viruses and other invaders, and geneticists have harnessed it to alter DNA sequences in a process called gene editing. We used cryo-electron microscopy…