Skip to content
-
-
- Cryo-EM, HIV, Methods, Publications, Ribosome, Structures
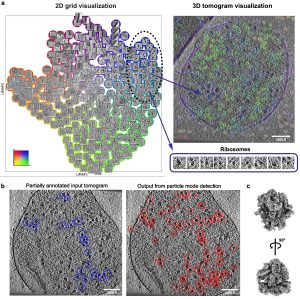
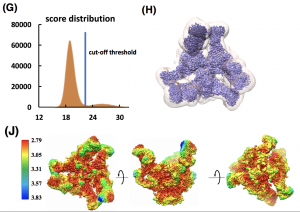
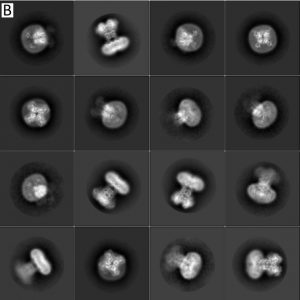
- In situ structure determination of conformationally flexible targets using nextPYP Single-particle cryoelectron tomography (SP-CET) is an imaging technique capable of determining the structure of proteins in their cellular environment at high-resolution. nextPYP is a web-based application designed to streamline the SP-CET structure determination process and facilitate the analysis of conformational variability. Here we explain how to use nextPYP-based methods…
-
-
- Publications, Structures
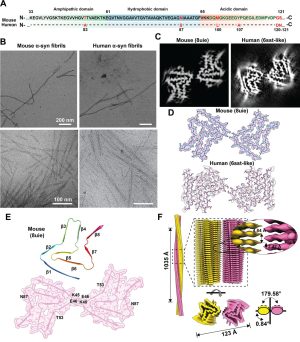
- Mouse α-synuclein fibrils are structurally and functionally distinct from human fibrils associated with Lewy body diseases The intricate process of α-synuclein aggregation and fibrillization holds pivotal roles in Parkinson’s disease (PD) and multiple system atrophy (MSA). While mouse α-synuclein can fibrillize in vitro, whether these fibrils commonly used in research to induce this process or form can reproduce structures…
-
-
- Cryo-EM, Machine learning and artificial intelligence, Membrane Proteins, Publications, Ribosome
- MiLoPYP: self-supervised molecular pattern mining and particle localization in situ Cryo-electron tomography (CET) allows the routine visualization of cellular landscapes in three dimensions at nanometer-range resolutions. When combined with single-particle tomography (SPT), it is possible to obtain near-atomic resolution structures of frequently occurring macromolecules within their native environment. Two outstanding challenges associated with CET/SPT are the automatic identification and…
-
-
- Publications, Structures
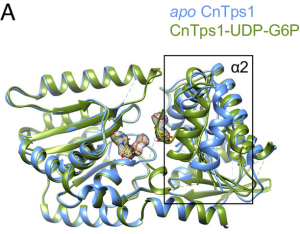
- Structures of trehalose-6-phosphate synthase, Tps1, from the fungal pathogen Cryptococcus neoformans: A target for antifungals Invasive fungal diseases are a major threat to human health, resulting in more than 1.5 million annual deaths worldwide. The arsenal of antifungal therapeutics remains limited and is in dire need of drugs that target additional biosynthetic pathways that are absent from humans. One…
-
-
- Publications, Structures
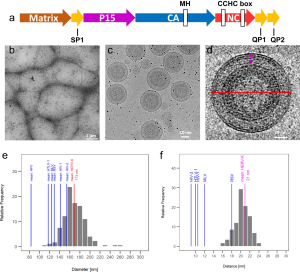
- Molecular architecture and conservation of an immature human endogenous retrovirus The human endogenous retrovirus K (HERV-K) is the most recently acquired endogenous retrovirus in the human genome and is activated and expressed in many cancers and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. We present the immature HERV-K capsid structure at 3.2 Å resolution determined from native virus-like particles using cryo-electron tomography and subtomogram…
-
-
- HIV, Publications, Structures
- Structural basis for breadth development in the HIV-1 V3-glycan targeting DH270 antibody clonal lineage Antibody affinity maturation enables adaptive immune responses to a wide range of pathogens. In some individuals broadly neutralizing antibodies develop to recognize rapidly mutating pathogens with extensive sequence diversity. Vaccine design for pathogens such as HIV-1 and influenza has therefore focused on recapitulating the natural…
-
-
- Publications, Structures
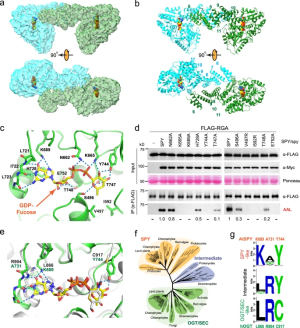
- Structure and dynamics of the Arabidopsis O-fucosyltransferase SPINDLY SPINDLY (SPY) in Arabidopsis thaliana is a novel nucleocytoplasmic protein O-fucosyltransferase (POFUT), which regulates diverse developmental processes. Sequence analysis indicates that SPY is distinct from ER-localized POFUTs and contains N-terminal tetratricopeptide repeats (TPRs) and a C-terminal catalytic domain resembling the O-linked-N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) transferases (OGTs). However, the structural feature that determines the…
-
-
- Publications, Ribosome, Structures
- Redox-sensitive E2 Rad6 controls cellular response to oxidative stress via K63-linked ubiquitination of ribosomes In this study, we set out to investigate the key role of Rad6 in regulating cellular response to stress in budding yeast as part of the RTU. Rad6 is small (20 kDa), highly conserved, and a multifunctional E2 involved in DNA repair and in the…
-
-
- Publications, Structures
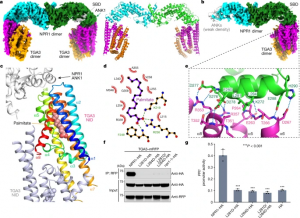
- Structural basis of NPR1 in activating plant immunity We report cryo-electron microscopy and crystal structures of Arabidopsis NPR1 and its complex with the transcription factor TGA3. Cryo-electron microscopy analysis reveals that NPR1 is a bird-shaped homodimer comprising a central Broad-complex, Tramtrack and Bric-à-brac (BTB) domain, a BTB and carboxyterminal Kelch helix bundle, four ankyrin repeats and a disordered salicylic-acid-binding…
-
-
- HIV, Membrane Proteins, Publications, Structures
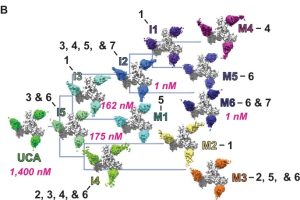
- Fab-dimerized glycan-reactive antibodies are a structural category of natural antibodies Natural antibodies (Abs) can target host glycans on the surface of pathogens. We studied the evolution of glycan-reactive B cells of rhesus macaques and humans using glycosylated HIV-1 envelope (Env) as a model antigen. We describe HIV-1 Env Fab-dimerized glycan (FDG)-reactive neutralizing Abs in HIV-1 vaccinated and simian-HIV (SHIV)-infected…
-
-
- CRISPR, Publications, Structures
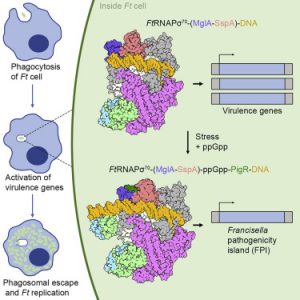
- Structural Basis for Virulence Activation of Francisella tularensis The bacterium Francisella tularensis (Ft) is one of the most infectious agents known. Ft virulence is controlled by a unique combination of transcription regulators: the MglA-SspA heterodimer, PigR, and the stress signal, ppGpp. MglA-SspA assembles with the σ70-associated RNAP holoenzyme (RNAPσ70), forming a virulence-specialized polymerase. These factors activate Francisella pathogenicity island…
-
-
- Publications, Ribosome, Structures
- Structural impact of K63 ubiquitin on yeast translocating ribosomes under oxidative stress K63 ubiquitination of ribosomes serves as a key regulator of protein production during cellular exposure to oxidative stress. Defining the structural and functional mechanisms of translation regulation would support the current understanding of critical reprogramming of eukaryotic gene expression. Our paper presents an examination of the structure…
-
-
- HIV, Publications, Structures
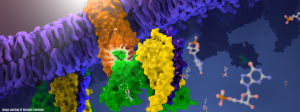
- Disruption of the HIV-1 Envelope allosteric network blocks CD4-induced rearrangements The trimeric HIV-1 Envelope protein (Env) mediates viral-host cell fusion via a network of conformational transitions, with allosteric elements in each protomer orchestrating host receptor-induced exposure of the co-receptor binding site and fusion elements. To understand the molecular details of this allostery, here, we introduce Env mutations aimed to…
-
-
- Membrane Proteins, Publications, Structures
- Single-particle cryo-EM structure of a voltage-activated potassium channel in lipid nanodiscs The structure of a voltage-activated potassium channel in lipid nanodiscs solved using cryo-electron microscopy is similar to previous X-ray structures, and provides insights into the mechanism of C-type inactivation. eLife, 7:e37558, 2018.
-
-
- Membrane Proteins, Publications, Structures
- Cryo-EM structure of human rhodopsin bound to an inhibitory G protein For the first time, scientists have visualized the interaction between two critical components of the body’s vast cellular communication network, a discovery that could lead to more effective medications with fewer side effects for conditions ranging from migraine to cancer. The near-atomic resolution images obtained, show a G-protein coupled…
-
-
- Publications, Structures, β-galactosidase
- Atomic Resolution Cryo-EM Structure of B-galactosidase We report methods to account for radiation damage and local changes in defocus and image drift, enabling visualization of atomic resolution features in a cryo-EM density map of inhibitor-bound -galactosidase, and derivation of atom-specific measures of local flexibility of the bound inhibitor using constrained molecular dynamics simulations. Structure, 26(6), p. 848-85, 2018.
-
-
- CRISPR, Publications, Structures
- Cryo-EM Structures Reveal Mechanism and Inhibition of DNA Targeting by a CRISPR-Cas Surveillance Complex Electron-microscopy images reveal how a CRISPR system marks specific DNA sequences for destruction. Microbes use CRISPR as a defense system to fend off viruses and other invaders, and geneticists have harnessed it to alter DNA sequences in a process called gene editing. We used cryo-electron microscopy…
-
-
- Cancer, Publications, Structures
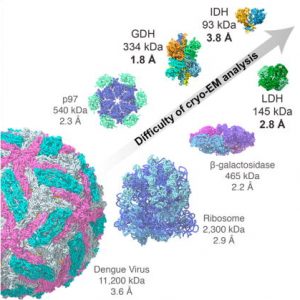
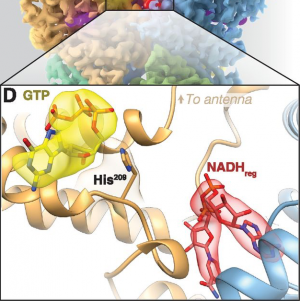
- Breaking Cryo-EM Resolution Barriers to Facilitate Drug Discovery Using cryo-EM we were able to capture images of glutamate dehydrogenase (GDH), an enzyme found in cells, at a resolution of 1.8 angstroms, a level of detail at which the structure of the central parts of the enzyme could be visualized in atomic detail. We also imaged two small proteins in…
-
-
- Cancer, Publications, Structures
- 2.3 Å Resolution Cryo-EM Structure of Human p97 and Mechanism of Allosteric Inhibition The protein p97 is an AAA adenosine triphosphatase (ATPase) that uses energy from ATP hydrolysis to regulate substrates involved in intracellular protein quality control. Its role in this central process makes it a target for cancer chemotherapy. We used cryo-electron microscopy to determine high-resolution structures for…
-
-
- Cancer, Publications, Structures
- Using Cryo-EM to Map Small Ligands on Dynamic Metabolic Enzymes: Studies with Glutamate Dehydrogenase Molecular Pharmacology, 89 (6) 645-651, 2016.
-
-
-
- Membrane Proteins, Publications, Structures
- Cryo-electron Microscopy Structures of Chimeric Hemagglutinin Displayed on a Universal Influenza Vaccine Candidate Chimeric hemagglutinin proteins are set to undergo human clinical trials as a universal influenza vaccine candidate, yet no structural information for these proteins is available. Using cryo-electron tomography, we report the first three-dimensional (3D) visualization of chimeric hemagglutinin proteins displayed on the surface of the influenza…
-
-
- Membrane Proteins, Publications, Structures
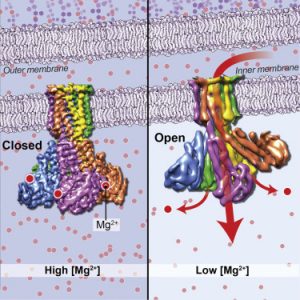
- Cryo-EM Structures of the Magnesium Channel CorA Reveal Symmetry Break upon Gating Magnesium ions (Mg2+) play essential roles in all living organisms. Bacteria and other prokaryotes rely upon the Mg2+-dependent channel CorA, which is composed of five identical subunits (A-E), to obtain these ions from their surroundings. Studies of CorA showed that, in contrast to most ligand-gated ion channels,…
-
-
- Publications, Structures, β-galactosidase
- 2.2 Å Resolution Cryo-EM Structure of β-galactosidase in Complex with a Cell-permeant Inhibitor Recent advances in cryo–electron microscopy allow structures of large macromolecules to be determined at near-atomic resolution. So far, though, resolutions approaching 2 Å, where features key to drug design are revealed, remain the territory of x-ray crystallography. Bartesaghi et al. achieved a resolution of 2.2 Å for a…
-
-
- Membrane Proteins, Structures
- Spatial Localization of the Ebola Glycoprotein Mucin-like Domain using Cryo-Electron Tomography J Virol, 88(18):10958-62, 2014.
-
-
- Membrane Proteins, Publications, Structures
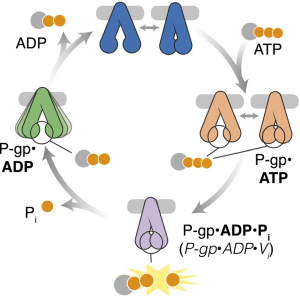
- Structural Mechanism of Glutamate Receptor Activation and Desensitization Understanding the structural basis of the transition from closed to active and desensitized conformations is central to deciphering the function of ionotropic glutamate receptors NMDA receptors, AMPA receptors, delta receptors, and kainate receptors as mediators of excitatory synaptic transmission in the central nervous system. Ligand binding at the receptor's extracellular surface…
-
-
- Publications, Structures, β-galactosidase
- Structure of β-galactosidase at 3.2-Å Resolution Obtained by Cryo-Electron Microscopy The vast majority of high-resolution structures obtained using cryo-EM have been typically restricted to large, well-ordered entities such as helical or icosahedral assemblies or two-dimensional crystals. We show here that emerging methods in single-particle cryo-EM now allow structure determination at near-atomic resolution, even for much smaller protein complexes with…
-
-
- HIV, Membrane Proteins, Publications, Structures
- Prefusion Structure of Trimeric HIV-1 Envelope Glycoprotein Determined by Cryo-Electron Microscopy HIV-1 Env transitions from a closed to an open state upon binding to its cellular receptor. Single-particle cryo-EM analysis now reveals the closed state of the HIV-1 Env trimer at ~6-Å resolution, featuring three gp41 helices at the center of the trimer. These findings indicate that HIV-1 enters…
-
-
- HIV, Membrane Proteins, Structures
- Molecular Architectures of Trimeric SIV and HIV-1 Envelope Glycoproteins on Intact Viruses: Strain-Dependent Variation in Quaternary Structure HIV and SIV contact and infect target T-cells following the binding of trimeric Env spikes displayed on the viral membrane with cellular receptors. The conformational changes in trimeric Env that are triggered by the interaction between trimeric Env and cell surface receptors…
-
-
- HIV, Membrane Proteins, Publications, Structures
- Molecular Architecture of Native HIV-1 gp120 Trimers We determined the structure of the native gp120 coat protein of HIV by cryo-electron tomography and molecular modelling. Comparison of gp120 structures in an unbound state, bound to a neutralizing antibody and bound to CD4 cell surface protein provides insight into the conformational changes that occur during antibody neutralization and attachment to…